xSuite Blog
Expert Knowledge on Digitalization & Automation of Business Processes

xSuite Blog
Expert Knowledge on Digitalization & Automation of Business Processes
What Does Cloud Native Mean?
Topic: Software Development and Implementation | Cloud
The term cloud native has been a popular buzzword in IT for some time now, and Google now delivers almost 4 million hits for this search term. Since 2015, there has even been a "Cloud Native Computing Foundation," which has the aim of advancing the cloud native philosophy and establishing it as a standard.
In this article we want to clarify the following questions: What is the exact meaning of the term? What are the hallmarks of cloud native solutions? And even more importantly: What benefits and advantages do cloud native solutions offer users?
Cloud native means: developed for the public cloud
The term cloud native can be better understood and classified if the beginnings of cloud computing are considered. Many of the first cloud solutions were developed on the basis of technologies already used in on-premises solutions. At the time, the cloud was not considered to be a leading form for delivering IT resources and software applications; rather, it was seen purely as an extension.
The cloud-native philosophy turns this approach upside down: Solutions that are cloud native have been specifically developed and optimized for operation in the cloud. They are designed to take full advantage of the technology offered by the cloud. The concept of cloud native computing not only refers to the architecture and the development process of software solutions, but also plays a central role in how the system is operated.
Software architecture: modular and open source
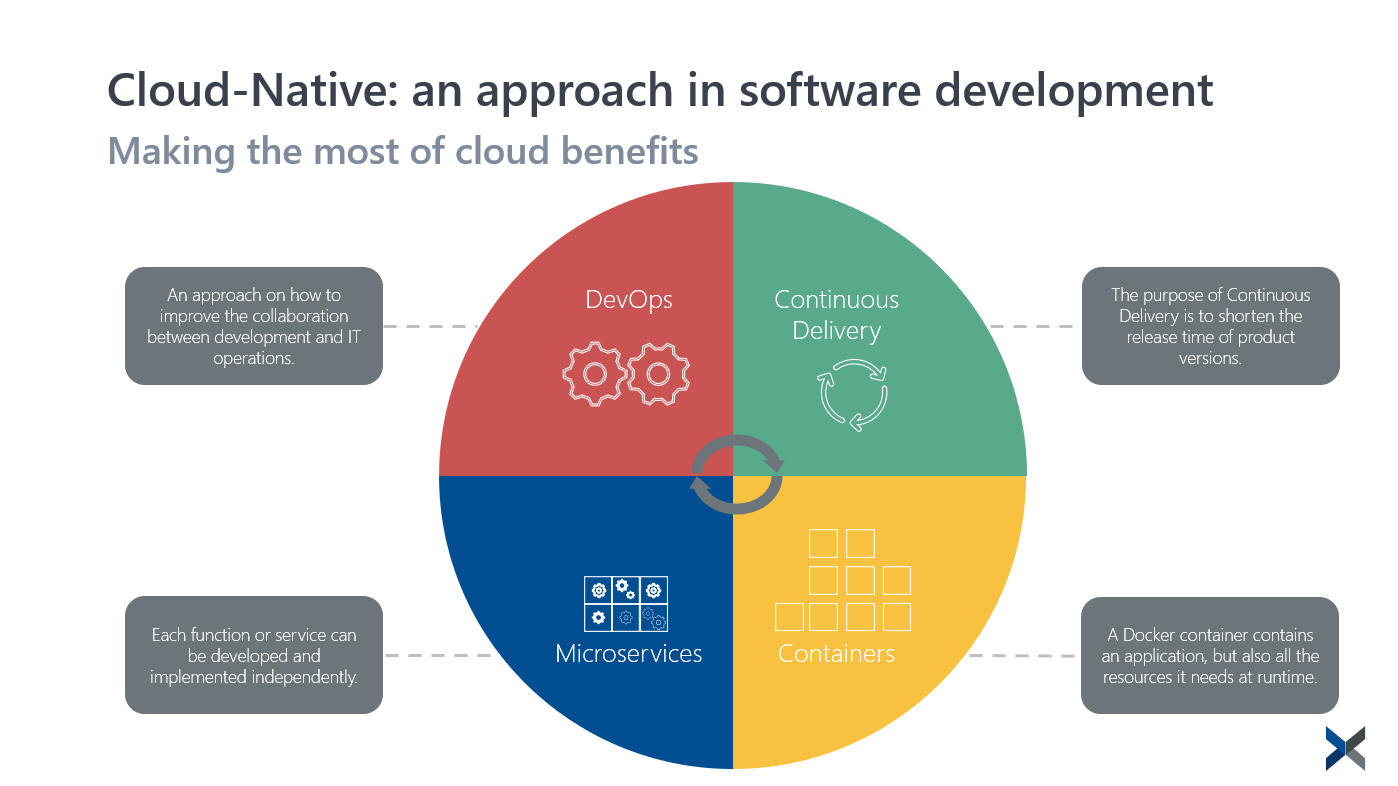
Public cloud solutions are designed to be used by a large number of different customers simultaneously, so they need to be particularly scalable. For this to be possible, the architecture of the software must be set up in such a way that bottlenecks never occur, even with a high load factor. Which is why cloud-native solutions rely on microservices and containers.
Speed is ensured by NoSQL databases, which often rely on open source technologies. A central feature of cloud-native solutions is the API (application programming interface), which provides for easy and seamless connection to other systems, be they local or in the cloud.
Software development: agile methods and processes
Integral to the idea of cloud technology is continuous development and rapid availability of new features. In order to perform at the tempo necessary, cloud-native solutions are not developed according to the classic waterfall model; rather, agile development methods and processes are used.
As a result, there are no longer any classic release cycles, such as once a year or once a quarter. Software development works in sprints and constantly delivers new program increments. This procedure is also known as continuous delivery.
Software operation: Development and IT administration work hand in hand
In classic development approaches, the software development and operation departments are strictly separated. With cloud-native solutions, it's the opposite: These departments work closely together in the form of a joint DevOps team (DevOps standing for "Development" and "Operations").
This allows new versions and functions to be tested and imported into the system much faster than with the traditional arrangement. Feedback can be incorporated much more quickly into the continuous development of a solution if operation and development work hand in hand. The constant, immediate import of new functions upon availability is also known as Continuous Deployment.
Advantages for users
Cloud-native solutions take full advantage of what the cloud has to offer. This makes them particularly scalable and performant. They are easy to use and are automatically kept up to date, so they can be a relief for the internal IT departments of companies. The availability of APIs makes them flexible and easy to integrate. As a result, they also enable hybrid scenarios.
If you would like to know more about the advantages of hybrid scenarios for document processes and in the ERP environment, I recommend the blog article of our managing director on the topic "Cloud First Is Not Cloud Only".
Topic
- AP Automation (28)
- Digitalization (28)
- SAP (18)
- Cloud (15)
- S/4HANA (10)
- E-Invoicing (9)
- Skills Shortage (6)
- Supplier Portal (6)
- AI and Machine Learning (5)
- Procurement (5)
- Invoice (5)
- GDPR (4)
- Software Development and Implementation (4)
- xSuite Group (4)
- Archiving (3)
- Usability and User Experience (3)
- RPA (2)
- Dynamic Discounting (1)
- Blockchain (1)
- Incoming Mail (1)


